
Lab Practical 1 introduces foundational concepts of anatomy and physiology, focusing on hands-on dissection, identification of anatomical structures, and understanding physiological processes through active learning techniques.
1.1 Overview of the Lab Practical
Lab Practical 1 in Anatomy and Physiology involves hands-on identification and exploration of anatomical structures, focusing on regional anatomy, skeletal, and muscular systems. Students engage in dissection, labeling, and describing physiological processes. The practical emphasizes active learning through tasks like identifying bones, attaching muscles, and understanding body regions. It also covers key physiological concepts, preparing students for clinical applications. The assessment evaluates both accuracy and understanding, with a minimum passing score of 50%. Resources like textbooks, manuals, and online tutorials are recommended for preparation. Community colleges, such as CCA, provide guidelines to ensure readiness, making this practical a foundational step in mastering human anatomy and physiology.
1.2 Importance of Lab Practicals in Anatomy and Physiology
Lab practicals are crucial for developing a comprehensive understanding of anatomy and physiology. They provide hands-on experience, enabling students to visualize and interact with anatomical structures, enhancing retention and spatial awareness. Practical sessions bridge theoretical knowledge with real-world applications, essential for healthcare professionals. Through dissection and identification exercises, students gain confidence in recognizing structures and their functions. Lab work also fosters critical thinking and patience, as seen in dissection-intensive tasks. Moreover, institutions emphasize lab preparedness, offering resources like manuals and digital tools to supplement learning. These experiences are vital for building a strong foundation in human anatomy and physiology, preparing students for clinical environments and patient care.
1.3 Key Objectives of Lab Practical 1
Lab Practical 1 aims to equip students with foundational skills in anatomy and physiology. The primary objective is to help students identify and describe major anatomical structures, such as bones, muscles, and organs. Students will learn to locate and label regions of the body, including the thorax, abdomen, and pelvis. Another key goal is to understand the relationships between structures and their physiological functions. Practical skills, such as handling dissection tools and specimens, are emphasized. Additionally, students will develop observation and critical thinking skills through interactive exercises. Mastery of these objectives ensures a solid foundation for advanced lab work and clinical applications in healthcare fields.
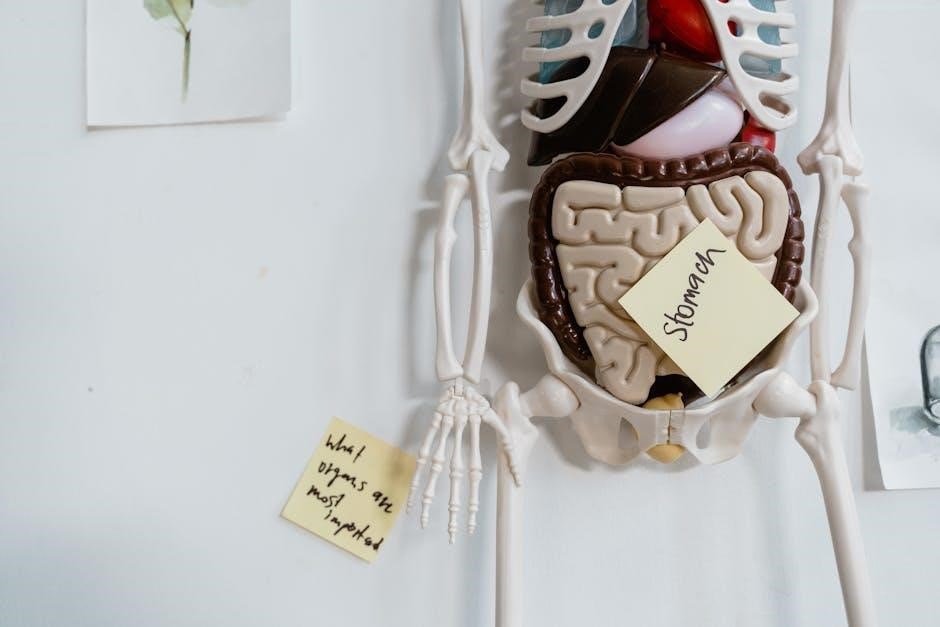
Preparation Strategies for the Lab Practical
Develop effective study habits, review course materials, and engage in active learning to build a strong foundation for the lab practical. Practical exposure and adequate practice enhance understanding and confidence.
2.1 Essential Study Materials and Resources
To excel in the lab practical, utilize a combination of textbooks, lab manuals, and digital resources. Key textbooks include “Human Anatomy and Physiology” by Elaine N. Marieb and “Anatomy and Physiology: An Integrative Approach” by Michael McKinley. Lab manuals provide detailed diagrams, dissection guides, and practice questions. Online platforms like Kenhub, Visible Body, and AnatomyTOOL offer interactive 3D models and quizzes. Flashcards, such as those on Quizlet or Anki, aid in memorizing anatomical terms and structures. Additionally, access virtual dissection software to practice identifying specimens digitally. Supplement your studies with practice exams and lab worksheets to familiarize yourself with the test format and content.
2.2 Effective Note-Taking and Review Techniques
Effective note-taking and review are crucial for success in anatomy and physiology lab practicals. Use a structured approach by organizing notes into categories like bone identification, muscle functions, and regional anatomy. Employ bullet points, diagrams, and flowcharts to simplify complex concepts. Review notes within 24 hours of class and use spaced repetition to reinforce memory. Highlight key terms and concepts for quick reference. Practice labeling diagrams and identifying structures from memory. Form study groups to quiz each other and clarify doubts. Utilize flashcards for quick revision and focus on understanding rather than rote memorization. Regular practice with past papers and online quizzes also enhances preparedness.
2.3 Utilizing Anatomical Models for Better Understanding
Anatomical models are invaluable tools for mastering complex anatomical structures in lab practicals. Hands-on interaction with 3D models enhances spatial awareness and clarifies relationships between body systems. Use detailed models to identify bones, muscles, and organs, focusing on landmarks and attachments. Digital models offer interactive features, allowing rotation and layer-by-layer exploration. Pair models with textbooks or diagrams to reinforce learning. Practice identifying structures independently before lab sessions to build confidence. Models also aid in visualizing physiological processes, making abstract concepts tangible. Regular use improves retention and exam readiness, ensuring familiarity with key structures during practical assessments.
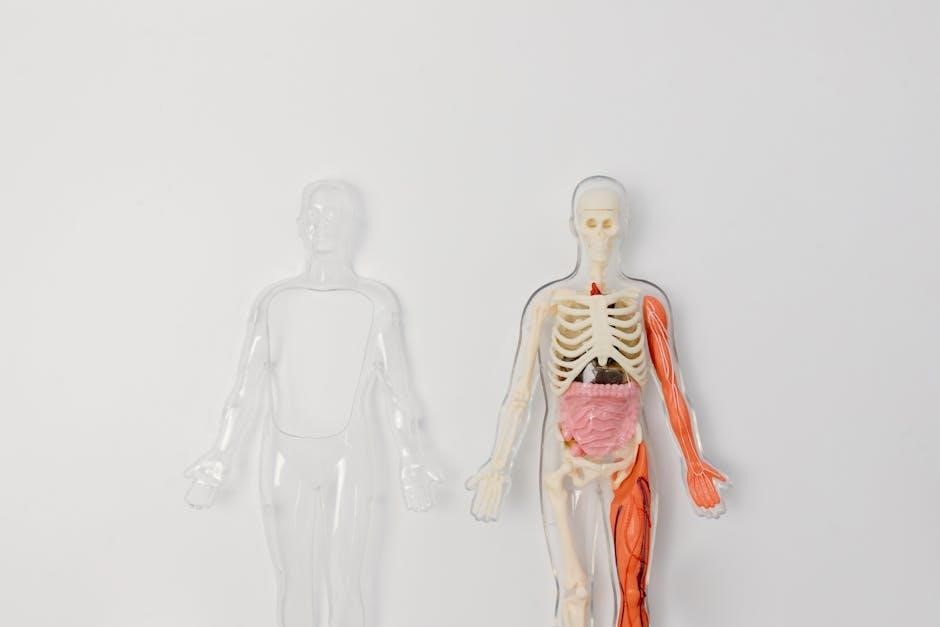
Key Concepts Covered in Lab Practical 1
Lab Practical 1 focuses on regional anatomy, skeletal and muscular systems, and physiological processes. Students identify structures, understand functions, and apply knowledge to real-world scenarios.
3.1 Regional Anatomy: Thorax, Abdomen, and Pelvis
Lab Practical 1 emphasizes regional anatomy, focusing on the thorax, abdomen, and pelvis. Students identify key structures, such as the heart, lungs, and diaphragm in the thorax, and organs like the liver, stomach, and intestines in the abdomen. The pelvis section covers reproductive organs, urinary bladder, and pelvic bone anatomy. Understanding spatial relationships between organs and tissues is crucial for accurate identification and labeling. This section also explores surface anatomy, enabling students to locate internal structures through external landmarks. Practical exercises involve identifying these regions on anatomical models and human specimens, reinforcing foundational knowledge essential for advanced studies in anatomy and physiology.
3.2 Skeletal System: Identification and Functions
Lab Practical 1 includes the identification and functions of the skeletal system, focusing on major bones and their classifications. Students learn to distinguish between long, short, flat, irregular, and sesamoid bones, such as the femur, humerus, carpals, and vertebrae. The functions of the skeletal system are emphasized, including support, movement, protection, blood cell production, and mineral storage. Key anatomical landmarks, like the skull, ribcage, and pelvis, are highlighted for their roles in protecting vital organs. Practical exercises involve identifying bones and their articulations, as well as understanding how they contribute to overall body structure and mobility. This section builds a foundational understanding of the skeletal system’s role in human anatomy.
3.3 Muscular System: Structure and Movement
Lab Practical 1 covers the muscular system, emphasizing the structure and function of muscles in movement. Students identify major muscle groups, such as skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscles, and their roles in voluntary and involuntary movements. The practical focuses on skeletal muscles, including their attachments to bones via tendons and their contribution to joint mobility. Key concepts include muscle origins, insertions, and actions, such as flexion, extension, and rotation. Exercises involve palpating muscles and observing their contractions. Understanding the muscular system’s role in locomotion, posture, and bodily functions is critical for this section, providing a hands-on approach to learning muscle anatomy and physiology.

Lab Procedures and Safety Protocols
Lab procedures ensure safe and effective learning environments. Students follow protocols for specimen handling, tool usage, and emergency preparedness to maintain safety and professionalism during practicals. Proper hygiene, personal protective equipment, and adherence to institutional guidelines are emphasized to prevent accidents and ensure compliance with health standards. Clear communication and teamwork are also stressed to foster a collaborative and secure workspace. These protocols are essential for conducting successful anatomy and physiology lab practicals. Always follow instructions provided by instructors and lab manuals to ensure a smooth and safe experience. Regular safety drills and orientations are conducted to prepare students for potential incidents. Familiarity with emergency exit routes, fire extinguishers, and first aid kits is mandatory. Students are encouraged to report any hazards or concerns immediately to prevent risks. Proper disposal of biological materials and chemicals is a critical aspect of lab safety. All equipment must be used correctly and returned to designated areas after use. Students are expected to respect shared spaces and maintain a clean workstation throughout the practical. Attendance in safety training sessions is compulsory for participation in lab activities. Understanding and adhering to these protocols ensures a safe and productive learning environment for all students. By following these guidelines, students can focus on achieving their learning objectives without unnecessary distractions or risks. Regular updates to safety protocols are communicated to students to keep them informed of any changes. Open communication between students and staff helps address any safety-related concerns promptly. Overall, safety remains a top priority in anatomy and physiology labs to protect both students and staff. Adhering to these protocols not only ensures individual safety but also contributes to the overall success of the lab practical experience. By taking safety seriously, students can engage fully with the material and gain the most from their lab sessions. A safe and well-prepared environment fosters academic excellence and hands-on learning opportunities. Safety protocols are regularly reviewed and updated to align with best practices in education and laboratory settings. Students are encouraged to take an active role in maintaining a safe environment by being vigilant and responsible. Lab assistants and instructors are always available to provide guidance and support during practicals. Their expertise ensures that students can navigate the lab confidently while adhering to safety standards. The importance of lab safety is reinforced through demonstrations, discussions, and hands-on training. Students are expected to demonstrate their understanding of safety protocols before participating in certain activities. This ensures that everyone is well-prepared and aware of their responsibilities. Safety is not just a set of rules but a shared commitment to creating a secure and effective learning space. By prioritizing safety, students can fully engage with the anatomy and physiology material and achieve their academic goals. The collective effort to maintain safety fosters a positive and productive atmosphere during lab practicals. Remember, safety is everyone’s responsibility, and active participation ensures a successful and enjoyable learning experience for all. Always approach lab activities with caution, respect, and attention to detail to minimize risks and maximize learning outcomes. Proper preparation and adherence to safety protocols are key to a successful anatomy and physiology lab practical experience. Stay informed, stay safe, and make the most of your time in the lab. Safety protocols are in place to protect everyone involved and ensure that the learning environment remains conducive to academic success. By following these guidelines, students can focus on mastering the material while maintaining a safe and respectful workspace. Safety should never be overlooked, as it forms the foundation of a productive and enjoyable lab experience. Stay proactive, stay informed, and contribute to a culture of safety in the anatomy and physiology lab. Remember, your safety and the safety of others are paramount in every lab activity. Always think ahead and take the necessary precautions to avoid potential hazards. A safe lab environment is essential for achieving educational goals and gaining valuable practical experience. By working together, students and staff can ensure that safety remains a top priority in every lab session. Stay alert, follow the protocols, and make the most of your time in the anatomy and physiology lab. Safety is not just a requirement; it’s a shared responsibility that benefits everyone involved. Take pride in maintaining a safe workspace and contribute to a positive and successful lab experience. Always be mindful of your surroundings and actions in the lab to ensure a safe and productive environment for yourself and others. Safety protocols are designed to protect and empower students, allowing them to focus on learning and achieving their full potential. By adhering to these guidelines, students can confidently engage with the material and develop essential skills in anatomy and physiology. Safety is the cornerstone of a successful lab experience, enabling students to explore and learn without unnecessary risks. Stay committed to safety, and you’ll be well on your way to excelling in your anatomy and physiology lab practicals. The importance of safety cannot be overstated, as it directly impacts the quality of the learning experience; Always prioritize safety and encourage others to do the same. A safe lab environment is a successful lab environment, where students can thrive and achieve their academic goals. Safety protocols are in place to ensure that every student has the opportunity to engage fully with the material while protecting their well-being. By taking safety seriously, students can make the most of their time in the anatomy and physiology lab. Remember, safety is not just a set of rules—it’s a commitment to excellence and responsibility in the pursuit of knowledge. Stay safe, stay focused, and make the most of your anatomy and physiology lab practical experience.
4.1 Setting Up the Lab Environment
Setting up the lab environment involves organizing workstations, ensuring proper lighting, and arranging essential tools and materials. Begin by sanitizing surfaces and equipment to maintain a sterile workspace. Place anatomical models, specimens, and charts within easy reach to facilitate observation and study. Assign specific areas for dissection tools, gloves, and protective gear to promote efficiency and safety. Labeling stations clearly helps students identify resources quickly. Ensure all electrical equipment is functioning and safely positioned. Prepare emergency supplies, such as first aid kits and fire extinguishers, and verify their accessibility. Finally, review the layout with students to ensure clarity and accessibility, fostering a conducive environment for hands-on learning and exploration. Proper setup minimizes distractions and maximizes productivity during lab sessions.
4.2 Handling and Care of Anatomical Specimens
Proper handling and care of anatomical specimens are crucial for maintaining their integrity and ensuring safe lab practices. Always wear gloves and protective gear when handling specimens to prevent exposure to preservatives like formaldehyde. Gently handle specimens to avoid damage, as rough handling can tear tissues or dislodge structures. After use, clean specimens with mild soap and water, then store them in designated containers with appropriate preservatives. Label containers clearly for easy identification. Regularly inspect specimens for signs of deterioration and report any damage to instructors. Follow institutional guidelines for disposal of biological waste to comply with safety and environmental regulations. Proper care extends the lifespan of specimens, ensuring they remain effective for educational purposes.
4.3 Safety Measures and Emergency Procedures
Safety measures are critical in anatomy and physiology labs to protect students and instructors from potential hazards. Always wear personal protective equipment (PPE), including gloves, goggles, and lab coats, when handling specimens or chemicals. Familiarize yourself with the location of emergency exits, fire extinguishers, and eyewash stations. In case of chemical spills, evacuate the area immediately and alert staff. For injuries, apply first aid and report incidents promptly. Regular drills ensure preparedness for emergencies like fires or chemical exposure. Adhere to proper protocols for handling sharp instruments and electrical equipment to minimize risks. Understanding emergency procedures ensures a safe and controlled learning environment.
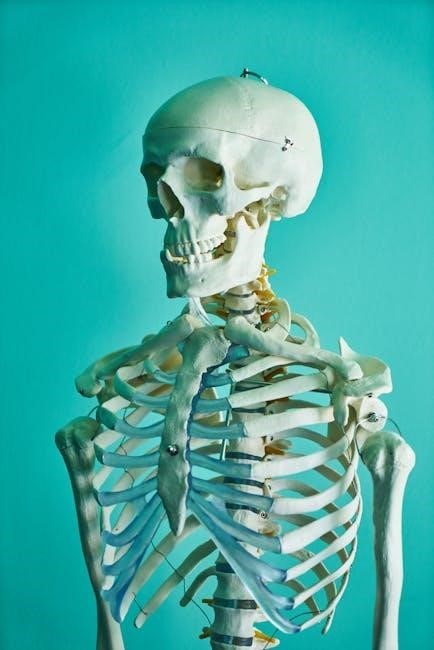
Common Lab Practical Questions and Answers
Students often ask about identifying bones, labeling body regions, and describing physiological processes. Practice answering these questions to improve your understanding and lab performance effectively.
5.1 Identifying Bones and Their Attachments
Identifying bones and their attachments is a critical skill in anatomy and physiology lab practicals. Students are often required to name bones, describe their shapes, and locate muscle and ligament attachments. For example, the femur (thigh bone) has distinct landmarks like the greater trochanter and condyles, which are essential for muscle attachment. Similarly, the humerus features the deltoid tuberosity and epicondyles. Common mistakes include confusing similar bones or misidentifying small details. To excel, students should study bone markings, practice with diagrams, and use 3D models to visualize attachments. Understanding these attachments is vital for grasping muscle function and movement, making it a foundational skill for lab success.
5.2 Labeling Regions of the Body
Labeling body regions accurately is a fundamental skill in anatomy and physiology lab practicals. The body is divided into major regions, such as the head, neck, thorax, abdomen, pelvis, and upper and lower limbs. Each region has subdivisions, like the axial and appendicular regions. Common mistakes include mislabeling or conflating similar regions. Students should practice using diagrams and 3D models to improve accuracy. Paying attention to anatomical landmarks, such as the clavicle for the thoracic region or the iliac crest for the pelvic region, aids in precise labeling. This skill is crucial for effective communication in healthcare and understanding physiological processes. Regular practice with labeled charts ensures mastery.
5.3 Describing Physiological Processes
Accurately describing physiological processes is essential for success in anatomy and physiology lab practicals. Students must demonstrate understanding of how body systems function, such as blood circulation, respiration, and digestion. Common challenges include confusing similar processes or missing key details. Effective descriptions should link structure to function and explain sequential steps. For example, explaining how oxygen moves from the lungs into the bloodstream requires clarity and precision. Utilizing flowcharts or diagrams can help visualize these processes. Practicing with case studies and lab simulations enhances descriptive skills. Mastery of physiological processes is critical for identifying normal versus abnormal functions, a key skill in healthcare professions.
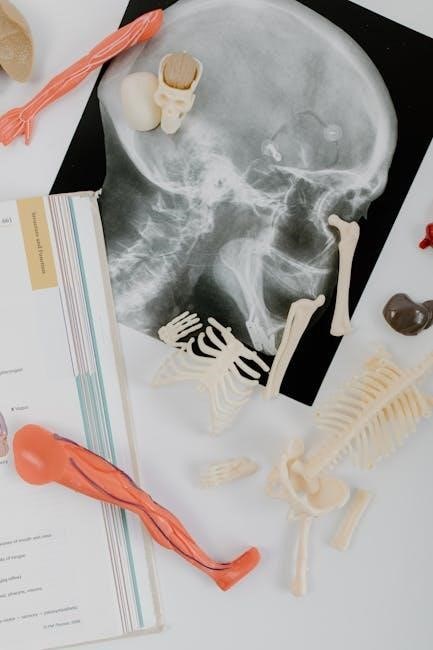
Dissection Techniques and Tools
Mastering dissection techniques and tools is vital for anatomy and physiology lab success. Essential tools include scalpels, forceps, and dissecting scissors, used for precise tissue exploration and identification.
6.1 Basic Dissection Tools and Their Uses
In anatomy and physiology lab practicals, basic dissection tools are essential for precise tissue exploration. Key tools include scalpels, used for making incisions, and forceps, which help in gripping and holding tissues. Dissecting scissors are utilized for cutting through connective tissue, while probes are used to locate and expose structures. Retractors are employed to separate and hold back tissue layers, providing better visibility. Magnifying glasses or dissecting microscopes aid in examining minute details. Proper handling and maintenance of these tools ensure effective dissection and safety. Understanding each tool’s function is crucial for successful lab outcomes and accurate identification of anatomical structures.
6.2 Step-by-Step Dissection Procedures
A successful dissection begins with proper preparation, including donning protective gear and setting up tools. Start by positioning the specimen to access the region of interest. Make initial incisions carefully, using scalpels to expose underlying structures without damaging them. Use forceps to gently separate tissues and retractors to maintain visibility. Systematically explore each layer, documenting observations. Identify key anatomical landmarks and note their relationships. Ensure precise cuts to avoid obscuring vital details. After completion, dispose of waste according to safety protocols and clean tools thoroughly. Following a structured, step-by-step approach enhances learning and ensures a comprehensive understanding of anatomical organization.
6.3 Preserving Dissection Specimens
Preserving dissection specimens is crucial for maintaining their integrity and longevity for future study. Common methods include formalin fixation, which prevents decay by cross-linking proteins, and ethanol preservation, which dehydrates tissues. Specimens can also be stored in sealed containers with preservative solutions to prevent contamination. Proper labeling and dating ensure easy identification. For long-term storage, specimens may be embedded in paraffin or frozen. Regular inspection and maintenance of stored specimens are essential to prevent degradation. Proper preservation techniques not only ensure safety but also allow for detailed examination and comparison during anatomy and physiology lab practicals, enhancing the learning experience for students.

The Role of Technology in Lab Practicals
Technology enhances anatomy and physiology lab practicals by providing interactive tools, 3D models, and virtual simulations, improving engagement and understanding of complex biological structures and processes.
7.1 Use of Digital Anatomical Models
Digital anatomical models revolutionize lab practicals by offering detailed 3D visualizations of human structures. These models enable students to explore complex anatomy interactively, enhancing spatial awareness and understanding. They often feature layered views, allowing users to peel back tissues and focus on specific systems. Interactive labels and descriptions provide immediate feedback, reinforcing learning. Digital models also simulate dissections, reducing the need for physical specimens and enabling repetitive practice. Additionally, they offer access to rare or hard-to-obtain anatomical variations, broadening exposure to diverse cases. These tools are particularly valuable for remote learning, ensuring consistent access to high-quality anatomical resources. They complement traditional methods, making anatomy and physiology education more engaging and accessible.
7.2 Virtual Dissection Software
Virtual dissection software provides a cutting-edge alternative to traditional dissection methods, offering immersive and interactive learning experiences. These programs allow students to digitally explore anatomical structures in 3D, with the ability to rotate, zoom, and layer tissues. Such tools are invaluable for anatomy and physiology lab practicals, as they enable repetitive practice without the need for physical specimens. Many platforms include guided tutorials, quizzes, and annotations to enhance understanding. Virtual dissection software also supports remote learning, allowing students to access labs anytime. It promotes engagement and deeper comprehension of complex anatomical relationships, making it an essential resource for modern anatomy education.
7;3 Interactive Learning Platforms
Interactive learning platforms are innovative tools that enhance anatomy and physiology education by providing engaging, dynamic experiences. These platforms often include interactive 3D models, quizzes, and simulations that allow students to explore complex anatomical structures in detail. Features such as real-time feedback, progress tracking, and collaborative learning opportunities make these platforms ideal for preparing for lab practicals. Many platforms also offer customizable content, enabling students to focus on specific areas of study. By integrating gamification and hands-on activities, interactive learning platforms foster a deeper understanding of anatomical concepts and improve retention. They are particularly useful for visual learners and those seeking additional practice outside traditional lab settings.
Assessment and Evaluation Criteria
Assessment evaluates students’ understanding of anatomical structures, identification accuracy, and practical skills. Grading focuses on precision, completeness, and adherence to lab protocols and safety standards.
8.1 Grading Rubrics for Lab Practicals
Grading rubrics for anatomy and physiology lab practicals are structured to assess student performance objectively. Criteria include accuracy in identifying anatomical structures, correctness in labeling, and clarity in describing physiological processes. Students are also evaluated on their ability to demonstrate dissection techniques and apply theoretical knowledge practically. Each criterion is assigned a specific weight, with identification accuracy often accounting for 40%, labeling for 30%, and descriptive answers for 30%. Rubrics provide clear expectations, ensuring consistency and fairness in grading. They also guide students on areas needing improvement, fostering better preparation for future assessments. Adherence to lab protocols and safety measures is also graded to emphasize professionalism and responsibility.
8.2 Common Mistakes to Avoid
Common mistakes in anatomy and physiology lab practicals often stem from poor preparation and inattention to detail. One frequent error is incorrect labeling of anatomical structures, which can lead to confusion and lost points. Students also mistakenly identify similar-looking bones or muscles, failing to note distinctive features. Improper use of dissection tools, such as applying too much pressure, can damage specimens. Additionally, neglecting to follow lab protocols, like not wearing gloves, can result in safety violations. Inadequate review of lab manuals and failure to practice identification techniques beforehand are other pitfalls. To succeed, students must double-check their work, seek clarification on uncertainties, and manage time effectively during the exam.
8.3 Feedback and Improvement Strategies
Feedback is a critical component of mastering anatomy and physiology lab practicals. Instructors often provide detailed insights into areas of strength and weakness, allowing students to refine their skills. To improve, students should review feedback meticulously and create targeted study plans. Focusing on misunderstood concepts and repeatedly practicing challenging structures can enhance performance; Utilizing review sheets and online resources to address gaps in knowledge is essential. Actively seeking clarification during lab sessions and engaging in peer discussions can also foster better understanding. By implementing these strategies, students can systematically address their weaknesses and achieve higher proficiency in subsequent lab practicals.
Institutional Approaches to Anatomy and Physiology Labs
Institutions implement structured anatomy and physiology lab programs, emphasizing hands-on training, safety protocols, and the integration of technology to enhance learning experiences and practical skill development.
9.1 Community College of Aurora (CCA) Guidelines
The Community College of Aurora (CCA) emphasizes a structured approach to anatomy and physiology lab practicum. Students are required to adhere to strict safety protocols, including proper handling of specimens and lab equipment. CCA provides comprehensive lab manuals and digital resources to ensure thorough preparation. The guidelines also stress active learning through group activities and peer-to-peer teaching. Instructors conduct regular assessments to evaluate understanding and technique. Students are expected to maintain professionalism, follow ethical standards, and respect anatomical materials. CCA’s guidelines also include specific checklists for pre-lab preparation and post-lab cleanup to ensure a smooth learning environment. Adherence to these policies is critical for academic success and lab safety.
9.2 Practical Nursing Program Requirements
The Practical Nursing Program requires students to complete anatomy and physiology lab practicals as a core component of their training. These labs focus on developing clinical skills, such as identifying anatomical structures and understanding physiological functions. Students must demonstrate proficiency in dissection techniques, specimen handling, and safety protocols. The program emphasizes accurate documentation of findings and adherence to ethical standards. Practical exams assess both theoretical knowledge and hands-on competencies. Students are also expected to participate in peer discussions and demonstrate professional conduct during lab sessions. Meeting these requirements ensures readiness for clinical rotations and future nursing practice. Regular feedback from instructors helps refine skills and address areas for improvement.
9.3 Academic Policies and Program Expectations
Academic policies for anatomy and physiology lab practicals require students to adhere to strict guidelines to ensure a productive and safe learning environment. Attendance is mandatory, and punctuality is emphasized to fully engage with lab activities. Students must submit all required assignments and reports on time, maintaining academic integrity. Professionalism and respect for peers and instructors are expected at all times. Confidentiality must be upheld when handling sensitive materials or data. Program expectations include active participation in discussions, adherence to safety protocols, and proper use of lab equipment. Students are also encouraged to seek clarification on any doubts to optimize learning outcomes. Failure to comply with these policies may result in disciplinary action or reduced participation in lab activities.
Additional Resources for Lab Preparation
Access recommended textbooks, online courses, and practice exams to enhance lab preparation. Utilize worksheets for hands-on practice and review key concepts effectively.
10.1 Recommended Textbooks and Manuals
Several textbooks and manuals are highly recommended for preparing for Anatomy and Physiology Lab Practical 1. “Gray’s Anatomy for Students” and “Anatomy: A Photographic Atlas” provide detailed visuals and descriptions. “Lab Manual for Anatomy & Physiology” by Elaine Marieb is tailored for hands-on learning, offering dissection guides and practice questions. Additionally, “Human Anatomy Lab Manual” by Kevin T. Patton includes interactive exercises and real-world applications. These resources are essential for understanding anatomical structures, labeling, and physiological processes. They also align with the content typically covered in Lab Practical 1, ensuring comprehensive preparation. Always cross-reference with your institution’s official lab manual for specific requirements.
10.2 Online Courses and Tutorials
Online courses and tutorials are invaluable for preparing for Anatomy and Physiology Lab Practical 1. Platforms like Khan Academy and Coursera offer free and paid courses that cover foundational concepts. edX provides university-level anatomy courses with interactive quizzes. Websites like LabSim and AnatomyTOOL offer virtual lab simulations, allowing students to practice dissection and identification of structures. Additionally, YouTube channels such as 3Blue1Brown and Crash Course present complex topics in an engaging, visual format. These resources complement traditional study materials and provide flexible learning opportunities. They are particularly useful for reinforcing key concepts and improving practical skills in a self-paced environment. Utilize these tools to enhance your preparation for the lab practical exam.
10.3 Practice Exams and Worksheets
Practice exams and worksheets are essential tools for reinforcing knowledge and assessing readiness for Anatomy and Physiology Lab Practical 1. Websites like Quizlet and Kenhub offer interactive quizzes and flashcards tailored to lab practical content. Lab Practical Workbooks often include labeled diagrams and short-answer questions to test identification and descriptive skills. Printable worksheets from educational platforms like Visible Body focus on regional anatomy, bone identification, and muscle functions. These resources help students familiarize themselves with exam formats and identify areas needing improvement. Regular use of practice exams and worksheets ensures better retention and confidence, ultimately leading to higher scores in the lab practical.